What Is Xxiv In Numbers
keralas
Sep 17, 2025 · 5 min read
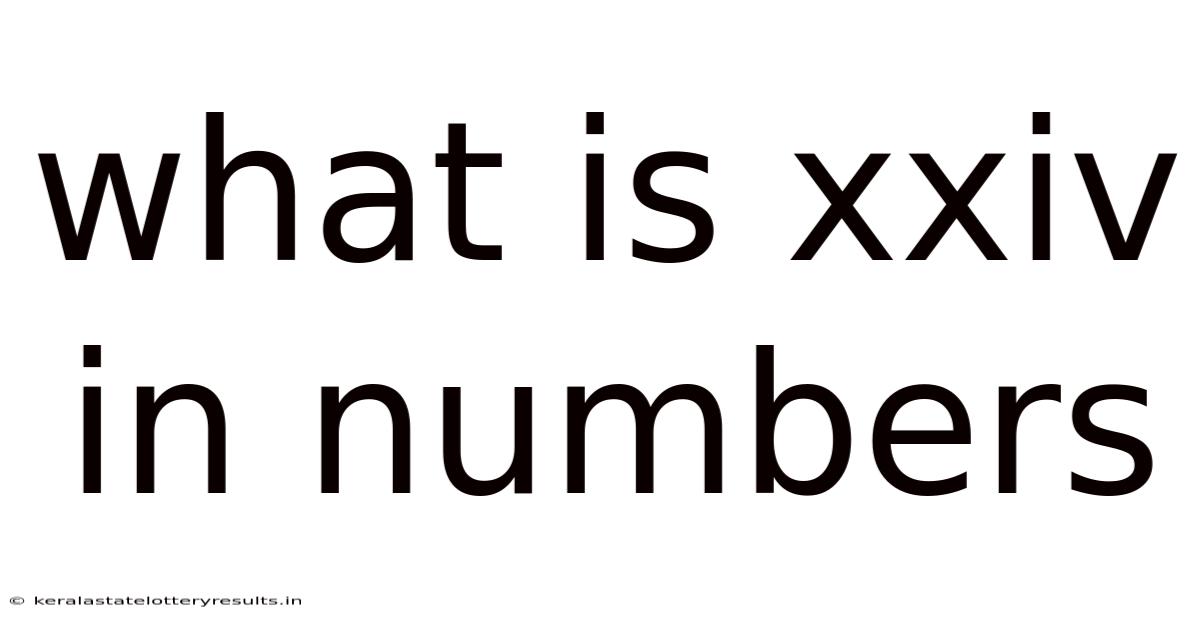
Table of Contents
What is XXIV in Numbers? Understanding Roman Numerals and Their Applications
Many of us encounter Roman numerals in various contexts – from clock faces and chapter headings to copyright dates and building inscriptions. Understanding Roman numerals isn't just about historical curiosity; it offers a glimpse into a fascinating system of numerical representation and its lasting influence. This comprehensive guide will explore the meaning of XXIV in numbers, explain the principles of the Roman numeral system, and delve into its historical significance and modern applications. We'll also address common questions and misconceptions surrounding this ancient numbering system.
Introduction to Roman Numerals: A System Based on Symbols
Unlike the decimal system (base-10) we commonly use, which is based on powers of 10 (1, 10, 100, 1000, etc.), the Roman numeral system uses a combination of letters to represent numbers. This system, developed in ancient Rome, relies on seven basic symbols:
- I = 1
- V = 5
- X = 10
- L = 50
- C = 100
- D = 500
- M = 1000
The beauty (and sometimes the challenge) of the Roman numeral system lies in its additive and subtractive principles. Let's break down how these principles work:
Additive Principle: Combining Symbols for Larger Numbers
The additive principle is straightforward. When a smaller numeral is placed before a larger numeral, the smaller numeral is added to the larger one. For example:
- VI = 6 (V + I = 5 + 1)
- XI = 11 (X + I = 10 + 1)
- LXV = 65 (L + X + V = 50 + 10 + 5)
Subtractive Principle: Subtracting for Efficiency
The subtractive principle introduces a level of sophistication. When a smaller numeral is placed before a larger numeral, the smaller numeral is subtracted from the larger one. This rule applies only to specific combinations:
- IV = 4 (V - I = 5 - 1)
- IX = 9 (X - I = 10 - 1)
- XL = 40 (L - X = 50 - 10)
- XC = 90 (C - X = 100 - 10)
- CD = 400 (D - C = 500 - 100)
- CM = 900 (M - C = 1000 - 100)
It's crucial to note that this subtractive principle is not applied arbitrarily. Only one smaller numeral can be subtracted from a larger numeral, and the smaller numeral must be one of the specific combinations listed above. For example, you wouldn't write IIX for 8; the correct representation is VIII.
Solving XXIV: Deconstructing the Roman Numeral
Now, let's tackle the central question: What is XXIV in numbers?
XXIV is composed of:
- X = 10
- V = 5
- I = 1
- I = 1
- I = 1
Applying the additive principle, we get: 10 + 5 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 24
Therefore, XXIV = 24.
Historical Context and Evolution of Roman Numerals
The Roman numeral system wasn't developed overnight. Its origins are unclear, with some theories tracing its development back to Etruscan numerals. Over time, the system evolved, with variations in usage and representation across different periods and regions. While convenient for certain applications, the Roman numeral system lacked the efficiency and flexibility of the positional decimal system that eventually replaced it in everyday calculations. The absence of a zero symbol presented significant challenges for arithmetic operations.
Modern Applications of Roman Numerals
Despite its limitations for complex arithmetic, Roman numerals persist in several modern contexts:
- Clock faces: Many analog clocks use Roman numerals for hours.
- Chapter headings: Books and other publications often use Roman numerals for chapter numbering.
- Copyright dates: You'll frequently see Roman numerals in copyright notices.
- Outlines and lists: Roman numerals can be employed to organize outlines and lists hierarchically.
- Building inscriptions: Roman numerals can be found on building facades and inscriptions, adding a touch of classical elegance.
- Monarchs and Popes: Kings, queens and Popes are often numbered using Roman numerals (e.g., Louis XIV).
- Super Bowl and Olympic Games: The naming and ordering of events use Roman numerals.
Common Misconceptions and Challenges
Understanding the subtle differences between additive and subtractive principles is critical to avoiding errors. Here are some common mistakes:
- Incorrect subtractive combinations: As mentioned earlier, only specific subtractive combinations are allowed. Using incorrect combinations leads to incorrect numerical values.
- Repeating symbols excessively: While you can repeat symbols like I, X, C, and M, there are limits to how many times you can repeat them before switching to a different representation for efficiency.
- Improper sequencing: Symbols must be arranged in descending order of value, except for the subtractive cases.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why are Roman numerals still used today?
A: Roman numerals maintain relevance due to their aesthetic appeal and traditional association with history and classicism. They are more suitable for stylistic purposes than for complex calculations.
Q: Are there limits to the numbers Roman numerals can represent?
A: Theoretically, there is no limit. However, for practical purposes, extremely large numbers become cumbersome and inefficient to express using Roman numerals.
Q: What is the largest number typically represented with Roman numerals?
A: While technically there's no upper limit, numerals exceeding a few thousand are rarely used due to the length and complexity. Numbers beyond M (1000) often involve overlining or special notations.
Q: How do I convert Roman numerals to Arabic numerals (our standard number system)?
A: By understanding the additive and subtractive principles outlined above, you can systematically convert Roman numerals to their Arabic equivalents. Break down the Roman numeral into its constituent parts, applying the rules to determine the numerical value.
Q: Can you use Roman numerals for decimals or fractions?
A: The traditional Roman numeral system doesn't directly support decimal or fractional values. Special notations were developed historically, but they are not widely used.
Conclusion: Appreciating the Roman Numeral System
While the Roman numeral system may not be as efficient as the decimal system for everyday arithmetic, it remains a fascinating and enduring part of our cultural heritage. Understanding its principles – both additive and subtractive – is key to correctly interpreting and using Roman numerals. From deciphering clock faces to appreciating historical inscriptions, knowledge of this ancient system opens up a window to history and demonstrates the evolution of mathematical representation. XXIV, representing the number 24, is but one small example of the enduring legacy of this symbolic numerical language. Remember, mastering Roman numerals isn’t just about knowing the conversion; it’s about appreciating the historical and cultural context that shapes their continued use.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 37 In Fahrenheit
Sep 17, 2025
-
Finding Roots Of Cubic Polynomials
Sep 17, 2025
-
2 4 Into A Decimal
Sep 17, 2025
-
Gcf Of 42 And 60
Sep 17, 2025
-
Lcm Of 15 And 8
Sep 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Xxiv In Numbers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.