X C V I I
keralas
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
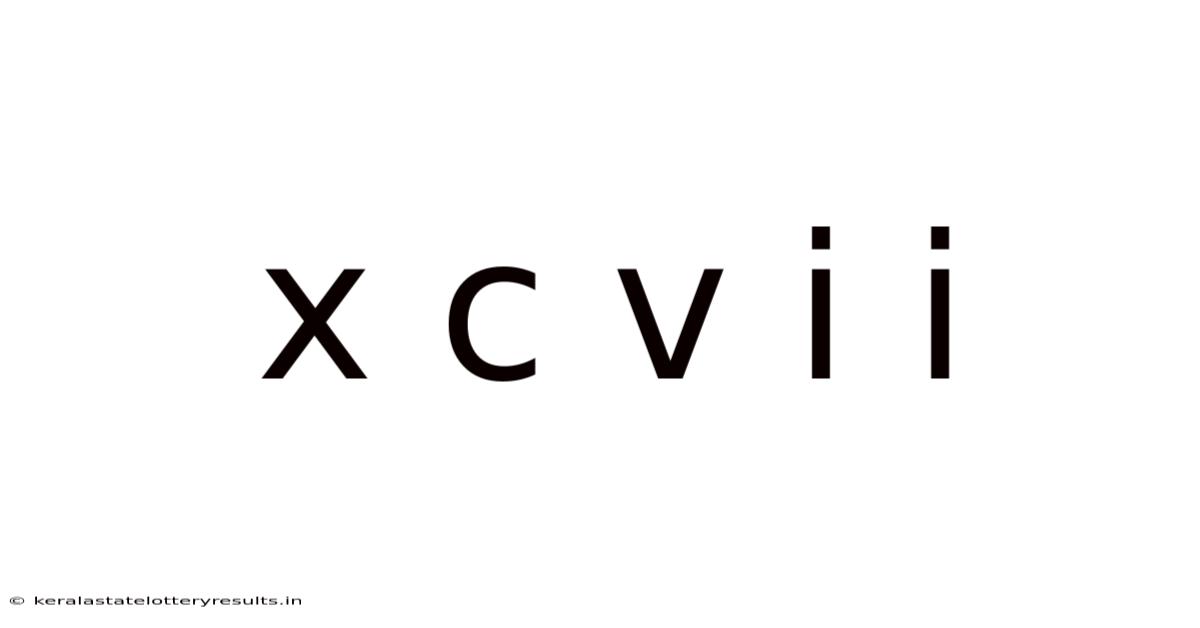
Table of Contents
Unraveling the Mystery: XCVII and the Roman Numeral System
The seemingly simple combination of letters – XCVII – might initially appear cryptic, but it represents a fascinating intersection of history, mathematics, and language. This article delves deep into the meaning of XCVII, exploring its numerical value, the historical context of the Roman numeral system, its applications, and common misconceptions. We'll unpack the logic behind this system and equip you with the knowledge to decipher other Roman numerals with ease. Understanding XCVII unlocks a key to understanding a significant part of Western civilization's history and mathematical legacy.
Understanding Roman Numerals: A Historical Perspective
The Roman numeral system, developed in ancient Rome, wasn't just a numbering system; it was an integral part of their culture and administration. Unlike our modern decimal system (base-10), which uses positional notation (where the value of a digit depends on its place), Roman numerals are additive and subtractive. This system uses seven basic symbols:
- I = 1
- V = 5
- X = 10
- L = 50
- C = 100
- D = 500
- M = 1000
These symbols are combined to represent larger numbers. The key to understanding the system lies in its additive and subtractive principles. When a smaller numeral precedes a larger one, it's subtracted; otherwise, it's added. For example:
- IX = 9 (10 - 1)
- IV = 4 (5 - 1)
- XI = 11 (10 + 1)
- LX = 60 (50 + 10)
This system, while seemingly complex at first glance, allowed for efficient representation of numbers in everyday life, from recording transactions to marking dates and distances on Roman roads.
Deciphering XCVII: Step-by-Step
Now, let's break down XCVII step-by-step:
-
XC: The 'X' (10) precedes the 'C' (100). Following the subtractive principle, XC represents 100 - 10 = 90.
-
V: This symbol simply represents 5.
-
II: Two 'I's represent 2 (1 + 1).
Therefore, XCVII = 90 + 5 + 2 = 97.
The Logic Behind Roman Numerals: Additivity and Subtractivity
The apparent simplicity of the Roman numeral system belies a subtle complexity. Its elegance lies in its use of both additive and subtractive principles. While mostly additive (e.g., adding values to get a total), the subtractive principle, using smaller numerals preceding larger ones, introduced a level of conciseness and efficiency. This feature, though seemingly arbitrary at times, is crucial for understanding the system's functionality. It prevented the need for excessive repetition of symbols; for instance, representing 9 as 'VIIII' would be cumbersome compared to the more efficient 'IX'.
Applications of Roman Numerals: Then and Now
Throughout history, Roman numerals have found diverse applications:
-
Dating: Often used to represent years (e.g., MCMLIV for 1954), particularly in formal contexts like copyright notices or historical documents. Their use continues in some contexts today, though the Arabic numeral system is predominantly used.
-
Clocks and Watches: Many analog clocks and watches still use Roman numerals, often on their faces, adding a classic aesthetic. This tradition harkens back to the widespread adoption of the system in earlier eras.
-
Outlines and Numbering: Roman numerals are frequently used for outlining major sections in books, essays, or presentations. This provides a hierarchical structure, visually distinguishing major points from sub-points.
-
Monarch Designation: Historically, and sometimes in contemporary contexts, monarchs are denoted using Roman numerals (e.g., King George VI). This practice allows for clear distinction between rulers with the same name.
-
Architectural and Decorative Purposes: Roman numerals are sometimes used in architectural designs and decorative elements, contributing to a classical or historical aesthetic.
Common Misconceptions and Limitations
While Roman numerals possess historical significance and a certain charm, they also have limitations:
-
No Zero: The Roman system lacks a symbol for zero, a concept crucial for our modern mathematical operations. This absence significantly impacts the system's capacity for certain calculations.
-
Cumbersome for Large Numbers: Representing very large numbers becomes increasingly lengthy and unwieldy in the Roman system. The lack of a positional system means that symbols need to be repeated, leading to potentially long sequences of characters.
-
Ambiguity (in some cases): While generally clear, certain combinations could lead to ambiguity without established conventions. Careful writing and adherence to established rules are necessary for clear communication.
-
Difficulty in Arithmetic Operations: Performing arithmetic calculations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) directly using Roman numerals is significantly more challenging than with the decimal system. The additive and subtractive nature introduces complexity to these operations.
Exploring Variations in Roman Numeral Systems
While the standard Roman numeral system is widely known, subtle variations existed across different periods and regions of the Roman Empire. These differences were often minor but highlight the evolution and adaptation of the system. For example, certain inscriptions might deviate slightly from the standardized forms, or there might be regional preferences in the representation of specific numbers. However, these variations did not fundamentally alter the core principles of the system.
The Transition to the Arabic Numeral System
The Roman numeral system gradually gave way to the more efficient Arabic numeral system (the one we use today) during the Middle Ages. The positional nature of the Arabic system, along with the inclusion of zero, vastly simplified mathematical operations and allowed for the representation of much larger numbers with greater conciseness. The adoption of the Arabic system marked a significant advancement in mathematical notation and calculation, contributing greatly to the scientific and technological progress of later centuries.
XCVII in Context: Historical and Modern Applications
XCVII, representing 97, has found its place in various contexts throughout history and continues to appear today. It may have been used to denote quantities of goods, distances, years in specific historical periods, or even as a sequential identifier in records. In the modern era, it might appear in various applications as mentioned earlier: outlines, clocks, or even as a subtle stylistic choice in design. Its meaning remains constant, but its applications reflect the ever-changing contexts of human endeavor.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: What is the largest number that can be easily represented using Roman numerals?
A: While technically there is no upper limit, representing extremely large numbers becomes increasingly cumbersome. Numbers exceeding several thousand usually require excessive repetitions of symbols, diminishing the system's practicality.
- Q: Are there any rules for writing Roman numerals correctly?
A: Yes, certain conventions should be followed. Avoid writing a smaller numeral before more than one larger numeral (e.g., 'IC' is incorrect for 99, the correct form is 'XCIX'). Also, only one smaller numeral should precede a larger numeral within any given combination.
- Q: How can I convert Roman numerals to Arabic numerals and vice versa?
A: Converting Roman to Arabic numerals involves understanding the additive and subtractive rules. For Arabic to Roman, a systematic breakdown into the constituent powers of 10 and their corresponding Roman symbols is necessary. Online converters and practice exercises can help.
- Q: Why is the Roman numeral system still used today?
A: Despite its limitations, it persists for various reasons: aesthetic appeal in some contexts, historical significance, and its use for outlining or representing years.
Conclusion: XCVII and the Enduring Legacy of Roman Numerals
XCVII, a seemingly simple combination of letters, represents much more than just the number 97. It's a window into a rich history, revealing the ingenuity and limitations of the Roman numeral system. While the Arabic numeral system has largely replaced it in most mathematical and scientific contexts, the Roman system remains a testament to the enduring impact of ancient civilizations and a reminder of the fascinating evolution of numerical representation throughout history. Its continued use in certain contexts highlights its lasting cultural and aesthetic appeal. Understanding XCVII, therefore, offers a broader appreciation for the systems we use today and the historical foundations upon which they are built.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Gcf Of 15 And 24
Sep 13, 2025
-
What Times What Equals 112
Sep 13, 2025
-
What Is 34 C In Farenhuit
Sep 13, 2025
-
Compare Fractions With Different Denominators
Sep 13, 2025
-
Gcf Of 25 And 30
Sep 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X C V I I . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.