What Is 10 / 2
keralas
Sep 14, 2025 · 6 min read
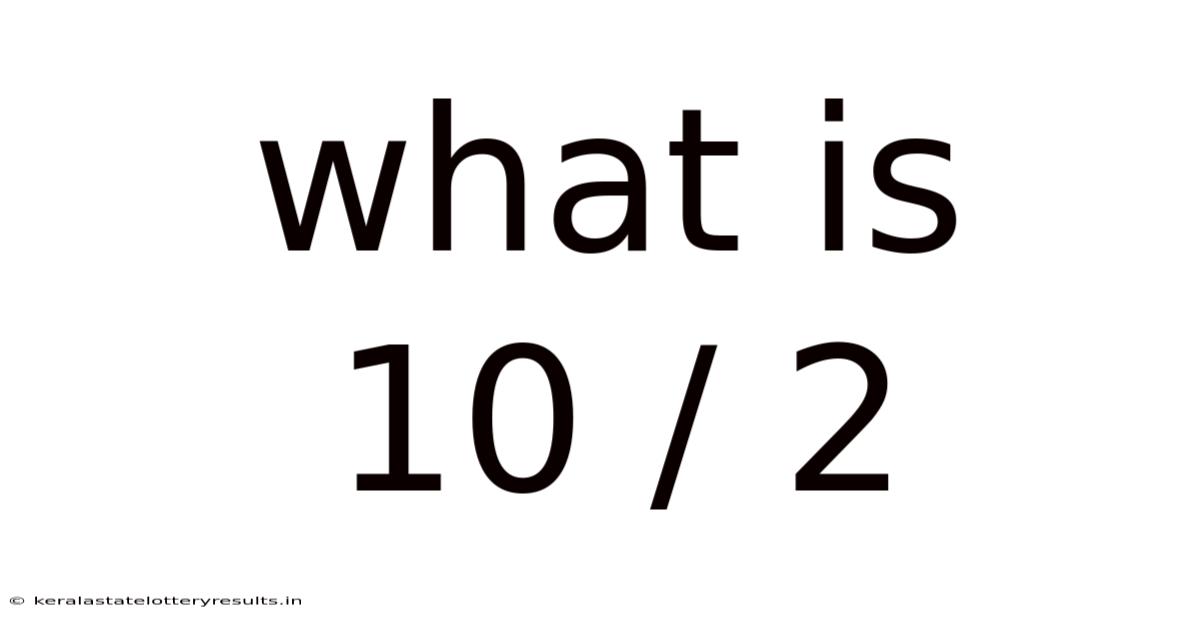
Table of Contents
What is 10 / 2? A Deep Dive into Division and its Applications
The seemingly simple question, "What is 10 / 2?", opens a door to a vast world of mathematical concepts. While the answer, 5, is immediately apparent to most, understanding the underlying principles of division reveals its fundamental importance in various fields, from everyday life to advanced scientific calculations. This article will explore the answer to this seemingly simple question, delving into the mechanics of division, its practical applications, and its significance within the broader context of mathematics.
Introduction: Understanding Division
Division is one of the four fundamental arithmetic operations, alongside addition, subtraction, and multiplication. It represents the process of splitting a quantity into equal parts or groups. In the expression 10 / 2, '10' is the dividend (the number being divided), '2' is the divisor (the number by which we are dividing), and '5' is the quotient (the result of the division). This equation can be read as "10 divided by 2 equals 5" or "how many times does 2 go into 10?".
The concept of division is deeply rooted in our daily lives. Imagine sharing 10 cookies equally among 2 friends. Each friend would receive 5 cookies, demonstrating the practical application of division. This seemingly simple act highlights the core principle: dividing a whole into equal parts.
Methods of Calculating 10 / 2
While the answer to 10 / 2 is straightforward, understanding different methods for solving division problems is crucial for developing a strong mathematical foundation. Here are several approaches:
-
Repeated Subtraction: This method involves subtracting the divisor (2) repeatedly from the dividend (10) until the remainder is 0. Each subtraction represents one group.
10 - 2 = 8 8 - 2 = 6 6 - 2 = 4 4 - 2 = 2 2 - 2 = 0
We subtracted 2 five times, therefore 10 / 2 = 5. This method visually demonstrates the concept of partitioning.
-
Multiplication's Inverse: Division is the inverse operation of multiplication. To find 10 / 2, we can ask: "What number, when multiplied by 2, equals 10?" The answer is 5 (2 x 5 = 10). This highlights the inherent relationship between multiplication and division.
-
Long Division: For more complex division problems, long division provides a systematic approach. While unnecessary for 10 / 2, understanding long division is essential for handling larger numbers and decimals. The process involves dividing the dividend digit by digit by the divisor, bringing down remainders, and placing the quotients appropriately.
-
Using a Calculator: Modern calculators provide a quick and efficient way to perform divisions. Entering 10 / 2 directly will yield the answer 5. While convenient, understanding the underlying mathematical processes remains critical.
Expanding the Concept: Beyond Simple Division
While 10 / 2 provides a simple example, the concept of division extends far beyond whole numbers. Let's explore some nuances:
-
Division with Remainders: When dividing whole numbers, sometimes the divisor doesn't divide the dividend evenly. For instance, 11 / 2 results in a quotient of 5 and a remainder of 1. This means we can create five groups of 2 with one left over. This is represented as 5 R1 (5 remainder 1).
-
Decimal Division: Division can also involve decimals. For example, 10 / 2.5 = 4. This involves working with decimal places and understanding how to shift decimal points during the division process.
-
Fractional Division: Dividing fractions involves a process of inverting the second fraction (the divisor) and multiplying. For example, 1/2 divided by 1/4 is equivalent to 1/2 multiplied by 4/1, resulting in 2.
-
Division by Zero: Division by zero is undefined. It's a fundamental rule in mathematics. Trying to divide any number by zero will result in an error, because it's impossible to divide something into zero groups.
The Significance of Division in Various Fields
Division is not merely a mathematical operation; it's a fundamental tool used across a multitude of disciplines:
-
Everyday Life: From splitting bills equally among friends to calculating fuel efficiency or determining the number of servings from a recipe, division is consistently applied in our daily lives.
-
Engineering and Physics: Division is integral to calculating speeds, forces, densities, and various other parameters in engineering and physics problems.
-
Computer Science: Division plays a crucial role in algorithm design, data structures, and various computational tasks. Many programming languages have built-in division operators.
-
Finance and Economics: Calculating interest rates, profit margins, and ratios crucial in financial analysis all involve division.
-
Statistics and Probability: Division is used extensively in calculating averages, frequencies, and probabilities.
-
Chemistry: Stoichiometry, which involves calculating the amounts of reactants and products in chemical reactions, heavily relies on division.
Real-World Applications of Division: Case Studies
Let's examine specific real-world scenarios that illustrate the practical use of division:
Scenario 1: Sharing Resources Equally: A group of 20 friends wants to share a pizza with 10 slices equally. Each friend will receive 10 / 20 = 0.5 slices of pizza.
Scenario 2: Calculating Speed: A car travels 120 kilometers in 2 hours. Its average speed is 120 / 2 = 60 kilometers per hour.
Scenario 3: Determining Unit Price: A pack of 12 pens costs $6. The price per pen is $6 / 12 = $0.50.
Scenario 4: Calculating Averages: A student scores 80, 90, and 70 on three tests. Their average score is (80 + 90 + 70) / 3 = 80.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What happens if I divide by a number larger than the dividend?
A: The result will be a number less than 1, often expressed as a decimal or fraction. For example, 10 / 20 = 0.5 or 1/2.
-
Q: Can I divide negative numbers?
A: Yes, the rules of signs apply. Dividing a positive number by a negative number results in a negative number, and vice versa. Dividing two negative numbers results in a positive number.
-
Q: How do I divide fractions?
A: To divide fractions, you invert the second fraction (the divisor) and then multiply the two fractions.
-
Q: What is the relationship between division and fractions?
A: Division can be represented as a fraction. For example, 10 / 2 can be written as 10/2, which simplifies to 5. This emphasizes the connection between division and representing parts of a whole.
-
Q: Why is division by zero undefined?
A: Division by zero is undefined because it leads to contradictions and inconsistencies within the mathematical system. There is no number that can be multiplied by zero to result in a non-zero number.
Conclusion: The Enduring Power of Division
The seemingly simple calculation, 10 / 2 = 5, serves as a gateway to a deeper understanding of the fundamental concept of division and its extensive applications. From the everyday act of sharing resources equally to complex scientific calculations, division underpins numerous aspects of our lives. Mastering this fundamental arithmetic operation is crucial for building a strong mathematical foundation and successfully navigating various fields of study and professional endeavors. The ability to grasp the underlying principles, including various methods of calculation, handling different number types, and understanding its limitations, allows for a more robust and complete understanding of this essential mathematical tool. The seemingly simple answer, 5, represents a powerful concept with far-reaching implications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Derivative Of Tan Squared X
Sep 14, 2025
-
Lcm Of 12 And 14
Sep 14, 2025
-
What Are The Factors 20
Sep 14, 2025
-
Lcm Of 11 And 13
Sep 14, 2025
-
Gcf For 55 And 77
Sep 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 10 / 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.